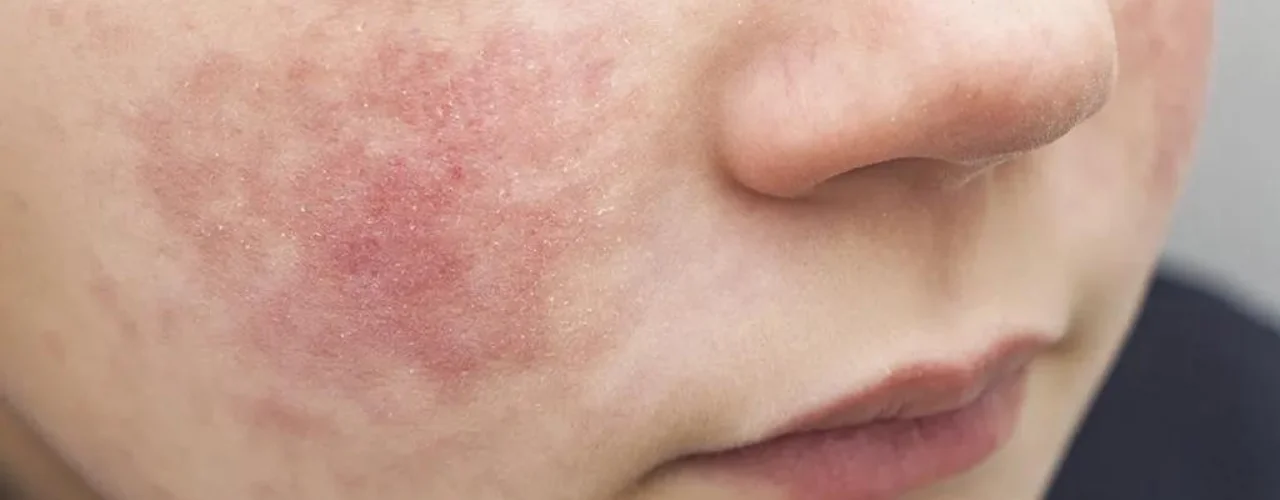
Atopic eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common chronic skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It is a type of eczema, a group of conditions that cause skin irritation. Atopic eczema often begins in childhood but can develop at any age. It is not contagious.
Causes of atopic eczema:
Atopic eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It’s the most common form of eczema, affecting 15-20% of children and 3-7% of adults worldwide. While the exact cause remains elusive, a complex interplay of genetics, immune system dysfunction, and environmental factors is believed to be responsible.

Genetic Predisposition:
- Atopic eczema has a strong genetic component. Studies have identified over 50 genes associated with the condition, with mutations in the filaggrin (FLG) gene being the most prominent risk factor. FLG encodes a protein crucial for maintaining the skin barrier. Mutations in FLG lead to a weakened barrier, allowing irritants and allergens to penetrate the skin and trigger inflammation.
- A 2011 study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that children with two copies of a mutated FLG gene were 30 times more likely to develop atopic eczema than those with no mutations.
Immune System Dysfunction:
- Atopic eczema involves an overactive immune response to allergens and irritants. This leads to the release of inflammatory chemicals that cause itching, redness, and swelling.
- T-helper 2 (Th2) cells play a key role in this process. They produce cytokines, like interleukin-4 and interleukin-13, which promote inflammation and IgE antibody production.
- A 2017 study published in Nature Genetics identified several genes involved in Th2 cell differentiation and activation, further solidifying the link between immune system dysfunction and atopic eczema.
Environmental Triggers:

- Several environmental factors can trigger or worsen atopic eczema, including:
- Dust mites: These tiny creatures are the most common environmental trigger for atopic eczema. Their feces and body parts contain allergens that can trigger an immune response.
- Pet dander: Skin flakes and saliva from pets, especially cats and dogs, can trigger atopic eczema in some individuals.
- Pollen: Seasonal allergies to pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds can worsen atopic eczema symptoms.
- Harsh soaps and detergents: These can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation.
- Food allergies: In some cases, certain foods, like milk, eggs, peanuts, and soy, can trigger or worsen atopic eczema symptoms.
Atopic eczema is a complex condition with no single cause. It’s likely a result of a combination of genetic susceptibility, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and preventive measures.
Symptoms of atopic eczema:
Atopic eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It’s the most common form of eczema, affecting 15-20% of children and 3-7% of adults worldwide.
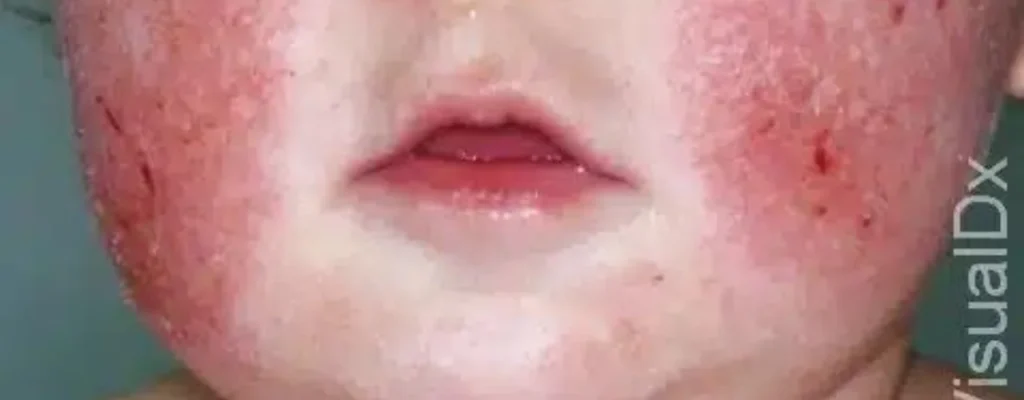
The symptoms of atopic eczema can vary widely from person to person, but some of the most common include:
- Dry, cracked skin: This is one of the most common symptoms of atopic eczema. The skin may appear flaky or scaly, and it may feel rough to the touch.
- intense itching: The itching associated with atopic eczema can be severe and constant. It can be difficult to resist scratching, which can worsen the symptoms.
- Red, inflamed skin: The affected areas of skin will be red and inflamed. The color may vary depending on your skin tone.
- Small fluid-filled bumps: In some cases, small fluid-filled bumps may develop on the affected skin. These bumps may weep or crust over.
- Thickened skin: Over time, the affected skin may become thickened and leathery.
- Oozing and crusting: In severe cases, the affected skin may ooze or crust over.
The location of the symptoms can also vary depending on the age of the person. In infants and young children, atopic eczema typically affects the face, scalp, and ears. In older children and adults, it is more common on the creases of the elbows and knees, the hands, and the feet.
Additional symptoms:
- Sleep problems due to itching
- Skin infections
- Anxiety and depression
It’s important to note that not everyone with atopic eczema will experience all of these symptoms. The severity of the symptoms can also vary from person to person. If you are concerned that you or your child may have atopic eczema, it is important to see a doctor or dermatologist for diagnosis and treatment.
Stages of Atopic Eczema: Understanding Its Progression
Atopic eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Its course can be described in three stages: acute, subacute, and chronic. While not everyone experiences all stages in the same order, a basic understanding of their progression can help manage symptoms and anticipate potential changes.
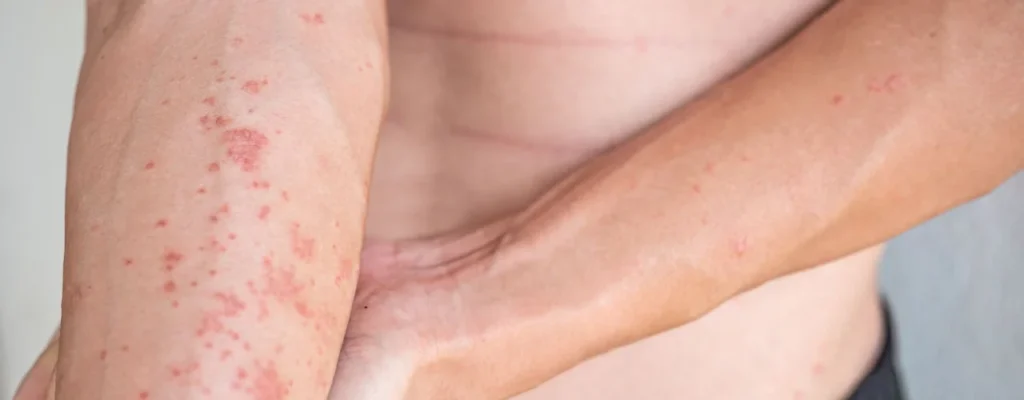
1. Acute Eczema:
- Onset: This is the initial stage, often triggered by an irritant or allergen.
- Symptoms: Intense itching, red, weeping blisters, oozing, crusting, swollen skin.
- Appearance: The affected area appears raw and inflamed, often with pinpoint red dots or oozing fluid.
- Duration: Typically lasts for days or weeks, depending on the severity and management.
2. Subacute Eczema:
- Transition: This stage follows the acute phase and marks the beginning of healing.
- Symptoms: Itching lessens, weeping and oozing subside, dry crusting appears, skin may feel thickened.
- Appearance: The affected area gradually loses its redness and raw appearance, transitioning to a scaly or crusty texture.
- Duration: Can last for weeks or months, depending on the individual and how well triggers are managed.
3. Chronic Eczema:
- Long-term: This stage represents the persistent form of the condition, often with recurring flare-ups.
- Symptoms: Dry, itchy skin, thickened plaques, darkened patches, possible scarring.
- Appearance: The affected area shows visible thickening and scaling, with potential pigmentation changes and scarring from long-term scratching.
- Duration: Eczema is a chronic condition with no cure, but proper management can minimize flare-ups and improve quality of life.
Remember:
- The stages of eczema can overlap and vary in progression for each individual.
- Identifying and managing triggers can help prevent or lessen the severity of flare-ups.
- Consulting a dermatologist is crucial for proper diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and long-term management strategies.
By understanding the different stages of atopic eczema, you can better anticipate changes in your condition, adapt your management approach, and work with your healthcare professional to achieve optimal skin health.
Treatment Approaches for Atopic Eczema:
Atopic eczema, commonly known as atopic dermatitis, lacks a definitive cure, but various treatment options can effectively manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Here’s an overview of the primary approaches, along with supporting scientific studies:
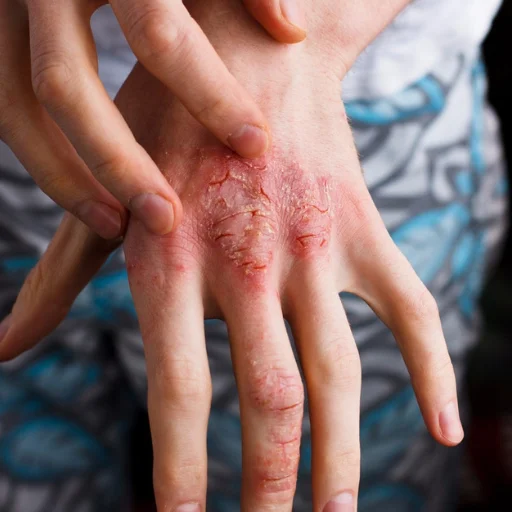
Moisturizers:
- Key benefit: Hydrate dry, itchy skin, restore the skin barrier, and prevent flare-ups.
- Study evidence: A 2012 study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology found that regular use of emollients (a type of moisturizer) significantly improved eczema symptoms and reduced the need for topical corticosteroids.
Topical Corticosteroids:
- Mechanism of action: Reduce inflammation, itching, and redness.
- Study evidence: A 2017 study in the British Journal of Dermatology demonstrated the effectiveness of topical corticosteroids in controlling moderate-to-severe eczema, with higher potency steroids showing better results.
Antihistamines:
- Target symptom: Alleviate itching, especially at night, leading to improved sleep.
- Study evidence: A 2020 Cochrane review concluded that oral antihistamines can provide moderate relief from itching associated with eczema, particularly beneficial for children.
Phototherapy:
- Mechanism of action: Utilizing ultraviolet (UV) light to suppress inflammation and improve skin barrier function.
- Study evidence: A 2019 study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found narrowband UVB phototherapy to be effective in treating moderate-to-severe eczema, with long-lasting benefits.
Immunomodulatory Therapies:
- Target process: Modify the immune system response to reduce inflammation.
- Study evidence: A 2023 study in The Lancet showed dupilumab, a biologic targeting the IL-4 and IL-13 pathways, to achieve significant and sustained improvement in adult eczema patients with inadequate response to conventional therapies.
Psychological and Behavioral Interventions:
- Focus: Address the emotional and behavioral aspects of living with eczema, like stress management and reducing scratching.
- Study evidence: A 2018 study in JAMA Dermatology found mindfulness-based cognitive therapy helpful in reducing anxiety and improving quality of life in adults with eczema.
Additionally:
- Dietary modifications: Identifying and eliminating food triggers in individuals with food allergies can improve eczema symptoms.
- Environmental control: Reducing exposure to dust mites, pet dander, and other environmental allergens can help prevent flare-ups.
Remember: Treatment plans should be personalized based on individual needs and disease severity. Consulting a dermatologist is crucial for diagnosis, tailored treatment, and monitoring progress.

Some additional tips for managing atopic eczema:
- Moisturize regularly: Apply moisturizer several times a day, especially after showering or bathing.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing: Avoid tight clothing that can irritate the skin.
- Protect your skin from the sun: Sun exposure can worsen eczema symptoms. Use sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
- Get enough sleep: Sleep deprivation can contribute to stress and worsen eczema symptoms. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep each night.
By following these tips and avoiding triggers, you can help manage your atopic eczema and live a comfortable life.
https://blog.derma.pk/?s=eczema
Conclusion:
Atopic eczema can be challenging, but with proper management and support, you can live a comfortable and fulfilling life. Remember:
- Consult a dermatologist for diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
- Identify and avoid your triggers.
- Practice gentle skincare habits.
- Manage stress and prioritize sleep.
- Seek support from healthcare professionals and patient communities.
By understanding atopic eczema and taking proactive steps, you can effectively manage this condition and enjoy healthy, vibrant skin.
Derma and Dental Clinic:
Location: Bahria Town, Lahore, Pakistan
website: Derma.pk
Esteemed Doctors:
- Prof. Dr. Tariq Rashid (Dermatology, 32 years of experience)
- Dr. Eram Razzaq (Dermatology, 15 years of experience)
- Dr. Navaira Tariq (Aesthetic Physician and Dental Surgeon)
- Dr. Ali Abu Bakar (Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon)
For Appointments:
- Online: Dermatology.pk
- WhatsApp: +923205999650
- Phone: 03041115000