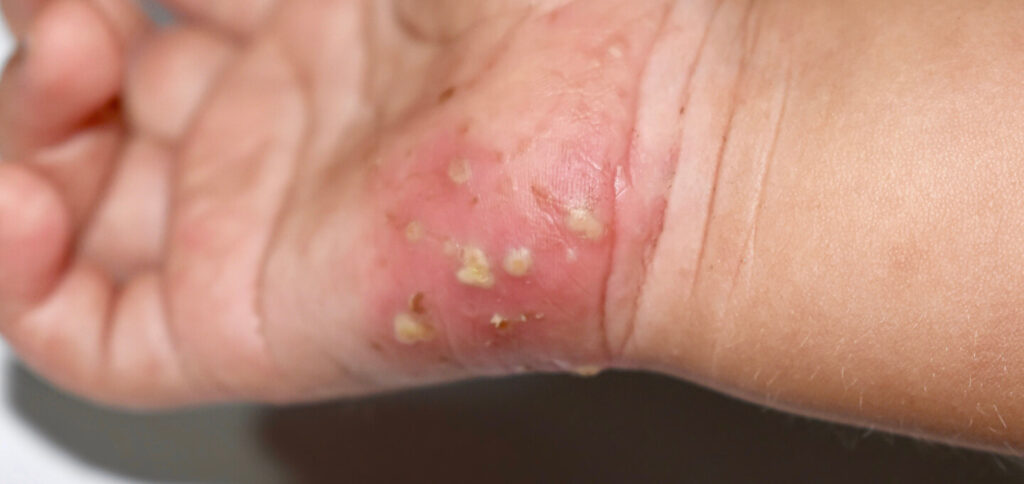
Scabies is a contagious skin condition caused by tiny mites called Sarcoptes scabiei. These mites burrow under the skin, lay eggs, and cause an itchy, blistering rash. While not inherently dangerous, scabies can be uncomfortable and spread easily through close contact.
Causes of scabies:
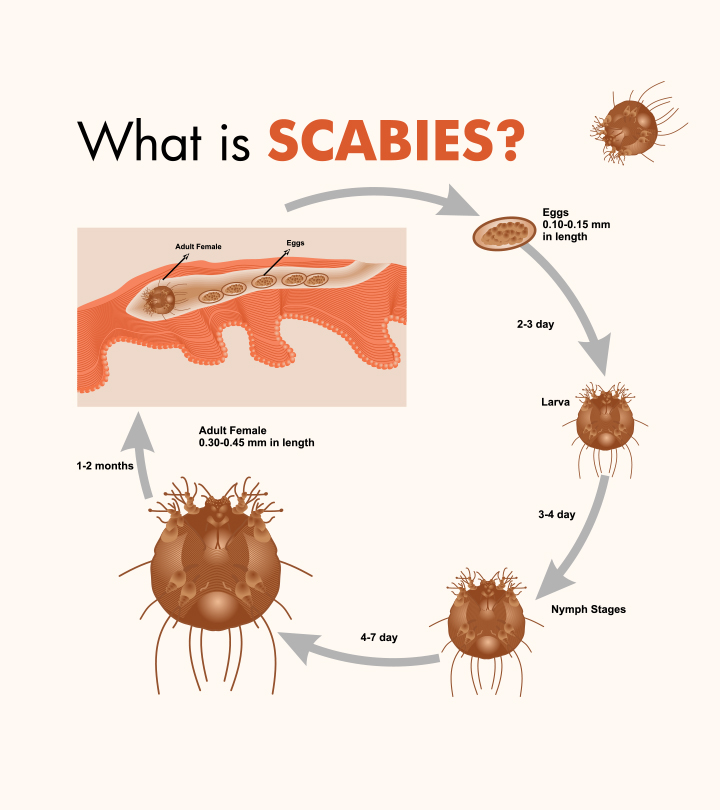
Scabies is caused by tiny mites called Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis. These mites are barely visible to the naked eye and burrow under the top layer of your skin, where they lay their eggs and live. The mite itself doesn’t cause much harm, but its presence and activities trigger your immune system to react, leading to the characteristic symptoms of scabies.
Here are the specific ways scabies gets transmitted:
Primary Cause:
- Direct, prolonged skin-to-skin contact: This is the main way scabies spreads, typically occurring during:
- Sexual activity
- Close household contact, especially among family members
- Prolonged physical contact in crowded settings like daycare centers or nursing homes
Secondary Causes (less common):
- Sharing contaminated personal items: Sharing bedding, clothing, or towels used by an infected person can transmit the mites, though this is less likely than direct contact.
- Indirect contact: While unusual, the mites can survive for a short time off the body, allowing for potential transmission through furniture or other surfaces touched by an infected person.
It’s important to note that:
- Casual contact like handshakes or hugs is unlikely to spread scabies.
- Pets cannot transmit human scabies, although they can have their own version of the mite.
- Scabies is not an airborne disease and cannot be spread through coughing or sneezing.
Understanding the causes is crucial for preventing its spread. If you suspect you or someone you know has scabies, it’s essential to seek immediate medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. They can prescribe effective medications and advise on necessary hygienic measures to prevent further transmission within your household or close contacts.
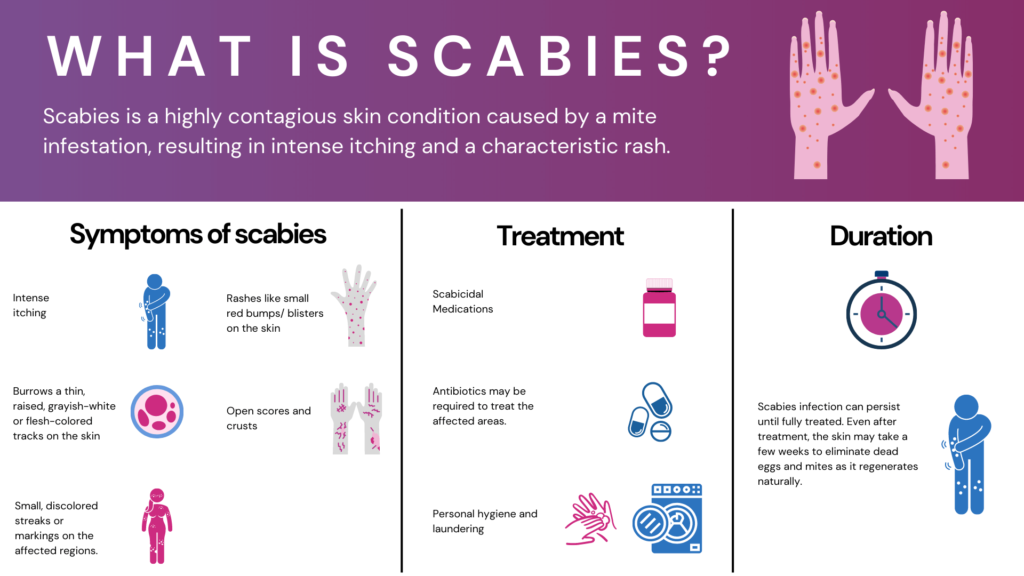
Symptoms of scabies:
Itchy skin condition caused by tiny mites called Sarcoptes scabiei. These mites burrow under the skin, lay eggs, and cause an irritating rash. While not inherently dangerous, scabies can be uncomfortable and spread easily through close contact.
Here are some common symptoms of scabies to be aware of:
- Intense itching: This is the most common symptom of scabies and is often worse at night or after a hot shower. The itching can be so intense that it disrupts sleep and makes it difficult to concentrate.
2. Tiny red bumps or blisters: These bumps and blisters typically appear on the hands, wrists, elbows, armpits, genitals, and buttocks. They may also be seen between the fingers and toes.
3. Scabs or crusting: Scratching the itchy bumps and blisters can lead to scabbing and crusting on the skin. This can be a sign of secondary infection, so it’s important to see a doctor if you notice this symptom.
4. Thin, burrow lines: These lines are created by the female mites as they burrow under the skin to lay their eggs. They are often seen between the fingers and toes, but they can also appear on other parts of the body.
Other symptoms: In some cases, scabies can also cause fever, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes.
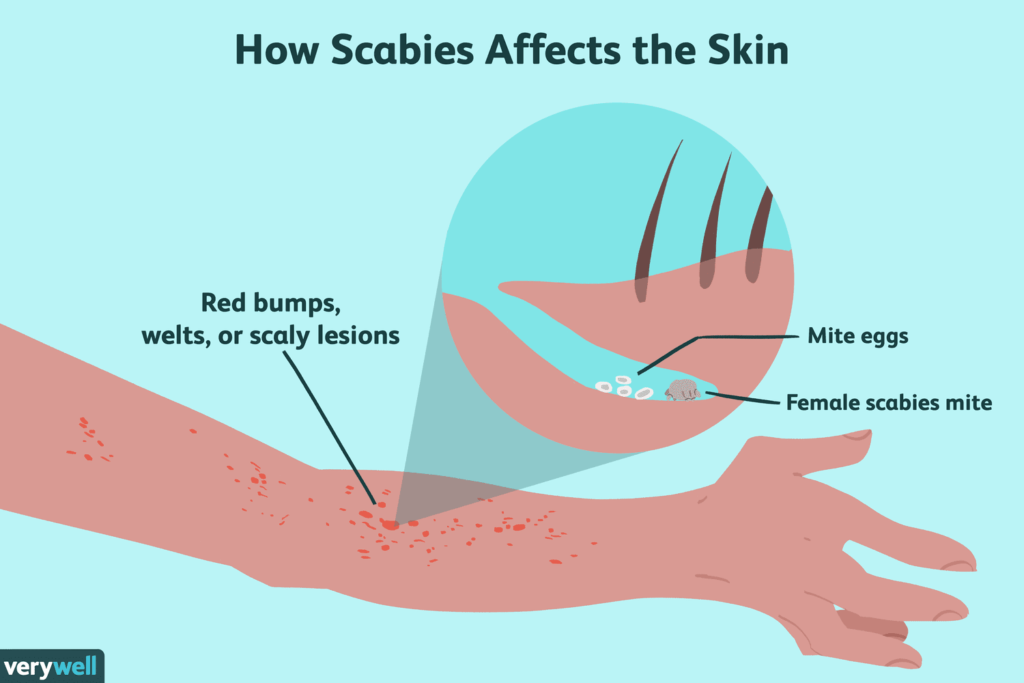
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a dermatologist to get a diagnosis and treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the spread of scabies and relieve discomfort.
Some additional things to keep in mind about scabies:
- Scabies is highly contagious and can be spread through close skin-to-skin contact.
- Sharing clothing, bedding, or towels with someone who has scabies can also transmit the infection.
- Scabies is treatable with prescription creams or lotions.
- It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions for treatment and to wash all bedding, clothing, and towels in hot water to prevent reinfection.
Transmission:
Scabies can be transmitted in a few different ways, but the main culprit is close, prolonged skin-to-skin contact with someone who has scabies. Here’s a breakdown of the key transmission routes:
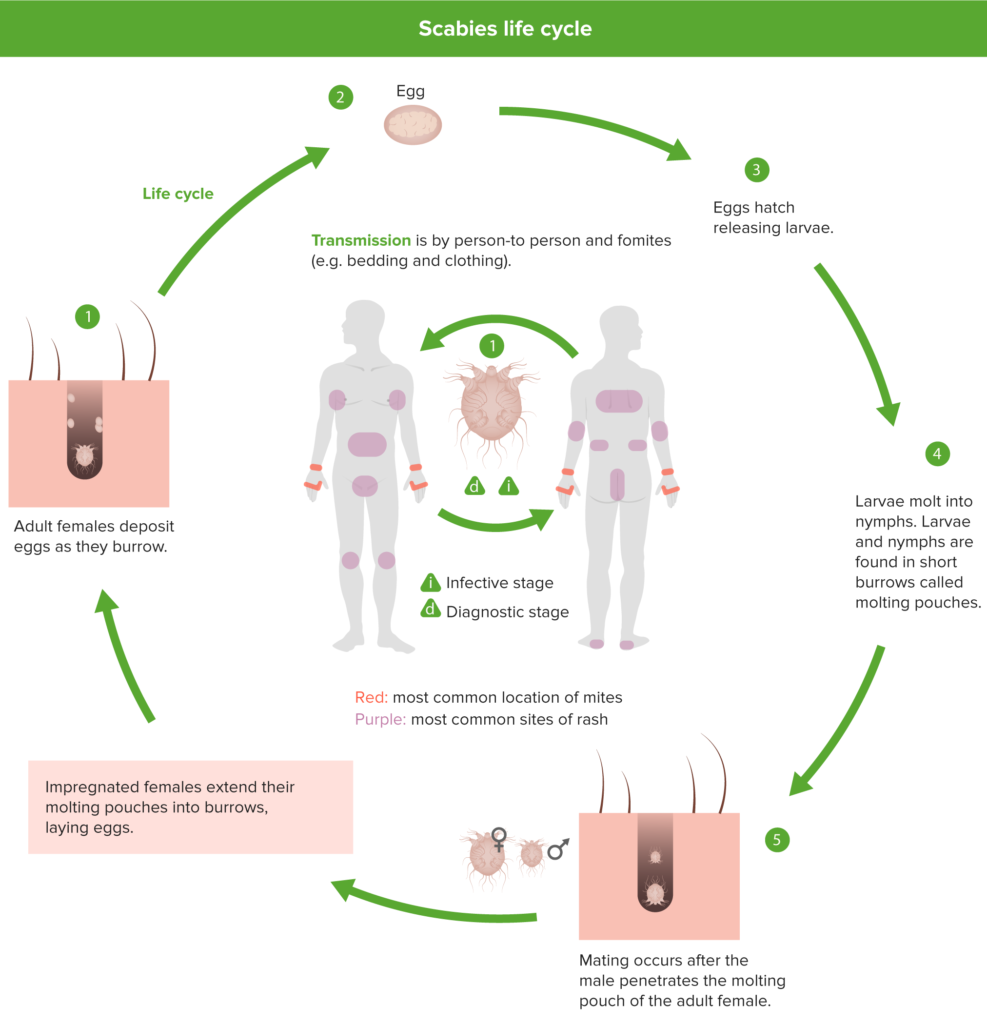
Main Route:
- Direct skin-to-skin contact: This is the most common way scabies spreads, particularly during:
- Sexual activity: Sexual partners are at high risk due to the intimate nature of contact.
- Close household contact: Family members who share beds, clothes, or towels are easily exposed.
- Prolonged physical contact in crowded settings: Daycare centers, nursing homes, and prisons can provide opportunities for transmission through activities like wrestling or cuddling.
Secondary Routes (less common):
- Sharing contaminated personal items: The mites can survive for a few days off the body, allowing for transmission through items like:
- Bedding: Sharing sheets, blankets, or pillows used by an infected person is a potential risk.
- Clothing: Clothes, especially undergarments or sleepwear, that come into contact with infested skin can harbor the mites.
- Towels: Sharing towels used by an infected person poses a small risk.
Other Points to Consider:
- Casual contact: Handshakes, hugs, or brief brushes against someone with scabies are unlikely to transmit the mites.
- Pets: Human scabies cannot be transmitted from pets, although they can have their own version of the mite.
- Airborne transmission: Scabies is not an airborne disease and cannot be spread through coughing or sneezing.
Remember:
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent the spread of scabies. If you suspect you or someone you know has scabies, seek immediate medical attention.
- Practice good hygiene: This includes frequent handwashing and avoiding sharing personal items like towels and bedding.
- Treat all close contacts: If someone is diagnosed with scabies, their sexual partners and household members should be treated even if they don’t have symptoms.
By understanding how scabies is transmitted, you can take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones from this itchy and potentially uncomfortable condition.
Treatment of scabies:
Scabies, while itchy and unpleasant, is thankfully quite treatable! Several options are available to eliminate the pesky mites and alleviate the symptoms. Here’s a breakdown of the primary treatment methods:
Medications:
- Prescription creams or lotions: These are the first line of defense against scabies. Common options include:
- Permethrin cream (5%): Most common, applied once or twice, effective for most cases.
- Crotamiton cream (10%): Applied twice, 24 hours apart.
- Sulfur ointment (5%): Applied daily for 3-5 days, safe for pregnant and breastfeeding women.
- Ivermectin (oral medication): Used in more severe cases or when topical treatments fail. Usually a single dose, sometimes repeated once or twice.
Additional Measures:
- Antihistamines: Oral or topical antihistamines can help control the itching and discomfort.
- Steroids: Topical steroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve scratching.
- Hygiene: Washing all bedding, clothing, and towels used by the infected person and their close contacts in hot water is crucial to prevent reinfection.
Treatment Tips:
- Follow your dermatologist instructions carefully regarding application frequency and duration for each medication.
- Treat all close contacts even if they don’t have symptoms to prevent them from spreading the mites further.
- Relieve the itching: Cool compresses, oatmeal baths, and loose clothing can provide temporary relief.
- Avoid scratching: Scratching can worsen the rash and lead to secondary infections.
- Be patient: Complete the prescribed treatment even if itching persists for a few weeks after the mites are gone.
Remember:
- Prompt diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing complications and spreading the infection.
- If you suspect you have scabies, consult your doctor immediately.
- With proper treatment and hygiene practices, scabies can be effectively eradicated.
https://blog.derma.pk/?s=scabies
Prevention of scabies:
Scabies might be itchy and unpleasant, but the good news is you can take steps to prevent it! Here are some key strategies to keep those pesky mites at bay:
Primary Prevention:
- Avoid close skin-to-skin contact: This is the key to prevention, especially during:
- Sexual activity: Practice safe sex and avoid intimate contact with anyone suspected of having scabies.
- Close household contact: Maintain good personal hygiene, avoid sharing beds, clothes, or towels, and encourage frequent handwashing.
- Crowded settings: Minimize close physical contact in daycare centers, nursing homes, or prisons.
Secondary Prevention:
- Practice good hygiene: This includes:
- Frequent handwashing with soap and water, especially after close contact with anyone, regardless of scabies suspicion.
- Keeping personal items clean: Wash your own clothes, towels, and bedsheets regularly in hot water and dry them on high heat. Avoid sharing these items with others.
- Maintaining a clean environment: Regularly clean and disinfect surfaces you frequently touch, like furniture and doorknobs.
Conclusion:
Scabies may be an itchy nuisance, but it’s far from invincible. By understanding its causes, transmission, and effective treatment options, you can take control and prevent its spread. Remember, early diagnosis, meticulous hygiene, and treating close contacts are key to banishing those pesky mites and reclaiming your scratch-free life.
Derma and Dental Clinic:
Location: Derma & Dental Clinic Bahria Town Lahore
website: Derma.pk
Esteemed Doctors:
- Prof. Dr. Tariq Rashid (Dermatology, 32 years of experience)
- Dr. Eram Razzaq (Dermatology, 15 years of experience)
- Dr. Navaira Tariq (Aesthetic Physician and Dental Surgeon)
- Dr. Ali Abu Bakar (Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon)
For consultation:
- WhatsApp: +923205999650
- Phone: 03041115000
- Website: Dermatology.pk



















Hi there, I found your website via Google while searching for a related topic, your website came up, it looks great. I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
Very educating story, saved your site for hopes to read more!
Magnificent beat ! I wish to apprentice at the same time as you amend your site, how could i subscribe for a weblog site? The account aided me a applicable deal. I have been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided vivid transparent idea